DIAMOND BUYING
Important Terms
- GIA: Gemological Institute of America—the leading independent Gemological laboratory in the U.S.A.
- EGL: European Gemological Laboratory—the leading independent Gemological laboratory in the world.
- AGS: American Gem Society
COLOR
Describes the amount of color the diamond contains. Ranges from colorless to yellow. Good color means no color.
EGL - GIA |
D E F |
G H I J |
K L M |
N O P Q R |
S T U V W X Y Z |
COLORLESS |
NEAR COLORLESS |
FAINT YELLOW |
VERY LIGHT YELLOW |
LIGHT YELLOW |
CLARITY
Describes the purity of the diamond. Most diamonds contain tiny natural marks called identifying characteristics or inclusions. The number of identifying characteristics or inclusions, their size, their nature and location all affect the diamond’s clarity grade.
CUT
Refers to the proportions, finish, symmetry and polish of the diamond. These factors influence the fire, brilliance, sparkle and beauty of a diamond. This is the only C controlled by a person, how well the cutter has perfected the cut.
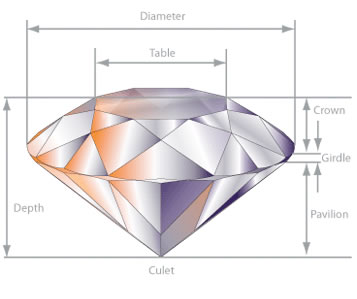
- Diameter The width of the diamond as measured through the girdle.
- Table This is the large, flat top facet of a diamond.
- Crown The upper portion of a cut gemstone, above the girdle.
- Girdle The narrow rim of a diamond that separates the crown from the pavilion. It is the largest diameter to any part of the stone.
- PavilionThe lower portion of the diamond, below the girdle. It is sometimes referred to as the base.
- Culet The tiny facet on the pointed bottom of the pavilion, which is the portion of a cut gem below the girdle.
- Depth The height of a gemstone, from the culet to the table.
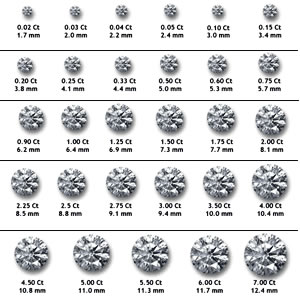
CARAT WEIGHT
A diamond's size is measured in carat weight. Each diamond carat is also equal to 100 points. For example, a diamond that is a 1/2 carat can also be referred to as a 50-point diamond. But keep this in mind: Bigger isn't necessarily better. A two-carat diamond that is cut poorly is not nearly as beautiful as a smaller diamond that's cut by a skilled diamond cutter. Or, it may be cut well, but have poor color and clarity.
Buyer Beware!
It is possible to influence the color of a diamond by irradiation treatment followed by heat treatment. This method is not recommended but is used to change the color of a diamond. The draw back of this treatment is that you risk color change over time.
Ten Facts You Need to Know Before buying a Diamond
- Never compromise on the cut. Cut determines the brilliance of the diamond
- Consider only certified diamonds by independent labs like AGS, GIA or EGI
- Fluorescence—What is good and bad. Know the difference.
- Be aware of treated diamonds—clarity and color enhancement.
- Only buy loose diamonds. None of the 4 C’s can be determined in a setting.
- Deal with an established reputable company, one who is a member of the American Gem Society (AGS). Less than 5% of the jewelers in America meet the high standards of this organization and are privileged to become members.
- Avoid “sales” or other promotions. The only thing discounted is the quality. How do you know what you’re getting.
- Know the return policy.
- Know the upgrade policy. No other jeweler offers 100% diamond trade-in with no additional investment required. House of Jewels does.
- Make sure that everything is written down so you know exactly what you are buying.
